The Userflow Debugger is your primary tool for troubleshooting why flows with auto-start conditions aren’t appearing when expected. This guide will walk you through using the Debugger to identify which conditions prevent your flows from starting.
Install the Userflow Chrome extension
The Debugger is part of the Userflow Chrome extension. If you do not already have the extension, install it from the installation page.
Launching the Debugger
Important
You must be in your app when you launch the Debugger. If you don’t launch the Debugger while viewing your app, it may result in a company not found error.
Open your app.
While viewing your app, click the Userflow Chrome extension icon (if pinned) in your browser toolbar, or the Extensions icon, to open the Debugger.
.png)
Grant access to the logged-in user following the instructions in the next section.
Granting Debugger access
Working with multiple environments in Userflow
If you have more than one environment in Userflow for your app (e.g., staging and production), the Debugger will always redirect to your primary environment by default. To use the Debugger in a secondary environment, first select the environment in Userflow, then grant the user access.
.png)
How to grant access
There are two ways to grant access to the Debugger tool for yourself or another user:
Userflow Settings: The best option when troubleshooting on behalf of another user.
Debugger Tool: The best option when troubleshooting with your own account.
Userflow settings
Log in to Userflow and select Settings > Debugger from the sidebar.
Click Add user.
Enter the name, email, or ID of the user.
The list of users in the Find user dropdown menu contains all users who have access to your application. Either select from the list or do a lookup as you type..png)
Click Add user.
Debugger tool
Launch the Userflow Debugger via the Chrome extension.
Click the Verify Setup dropdown menu.
Click the currently signed-in user link.
.png)
Click Grant access in Userflow. This will redirect you to the Debugger settings page in the Userflow builder. If the signed-in user already has access to the Debugger, this button will not show up.
.png)
Click Add user and confirm that the User ID is correct. The current browser session now has Debugger analysis capabilities enabled.
.png)
Checking auto-start conditions for a flow
With the Debugger open, click Check auto-start from the Debugger dropdown menu.
.png)
Select the specific flow you want to investigate from the Select flow dropdown menu. Only published flows will appear in the list.
.png)
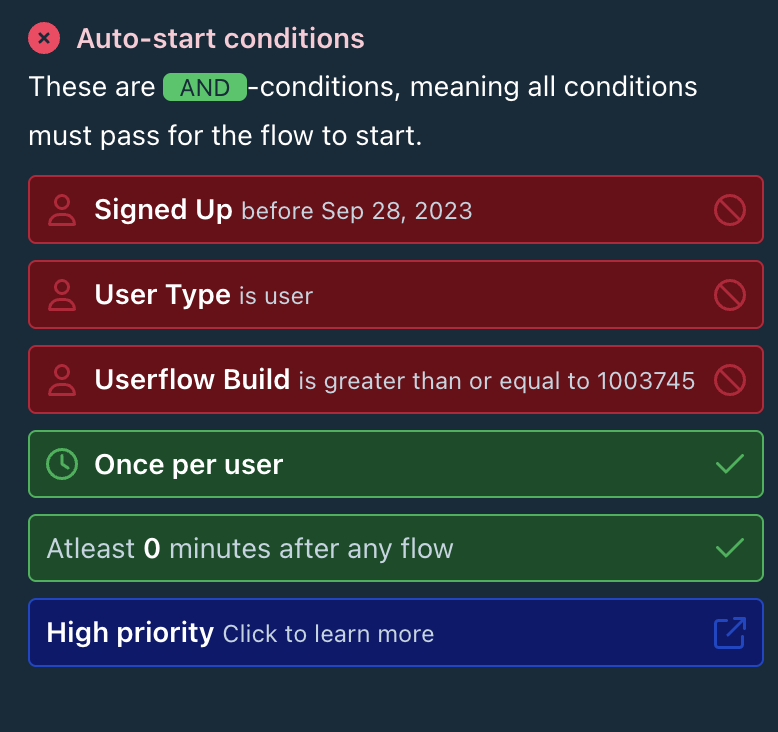
Understanding condition status
Once a flow is selected, the Debugger displays its auto-start conditions as colored “pills”. Each pill represents a condition or a group of conditions:
Color | Status | What it means |
|---|---|---|
🔴 Red | Failing | This condition is blocking your flow from starting. |
🟢 Green | Passing | This condition is currently met. |
🔵 Blue | Waiting | This condition is waiting for an action or a time constraint (e.g., waiting for user input, waiting for time to elapse before re-triggering) |
🟡 Yellow | Temporarily blocked | Temporary conditions are preventing the flow, often related to frequency or delays. Expand the pill to see the specific underlying conditions. |
Common auto-start conditions checked
The Debugger evaluates various conditions. Here are common issues that can block a flow:
Attribute: Checks if the current user or their company matches the specified User Attribute or Company Attribute filters. Requires attributes sent via Userflow.js, an integration (e.g., HubSpot), or the API.
Current page: Checks if the user is on the specific URL path defined in the condition.
Event: Checks if the user has performed the required tracked event. Events can be sent via
userflow.trackin Userflow.js or created using no-code Event Trackers.Segment: Checks whether the user is currently in the specified Segment.
Flow/Checklist: Checks the completion status (e.g., Completed, Seen) of another specified flow or checklist.
Element: Checks if a specific UI element (identified by a selector) is present or has been clicked in your application.
Text input value: Checks if a form input field contains a specific value entered by the user.
User fills in input: Checks if the user has entered any value into a specific input field.
Current time: Used for scheduling flows. Checks if the current date/time is before or after the configured time.
Wait: Checks whether the configured delay period has elapsed after all other conditions are met.
Frequency of trigger: Checks if the flow has already been shown based on limits like “Only show once” or recurrence settings.
Delay Start After Previous Flow: Checks if the required minimum time has passed since another specified flow was triggered.
Constrain flow to current company (Advanced Setting): If enabled, checks if the user’s current company context matches the one they had when they first qualified for the flow. Prevents triggering if the user switches companies during a session.
Flow Trigger Precedence
If multiple flows meet the auto-start conditions for a user simultaneously, Userflow applies the following tie-breaker rules to decide which one flow will be triggered:
Flows the user has never seen before are prioritized over flows they have seen.
If all eligible flows have been seen before, the one whose last occurrence was seen the longest time ago is prioritized.
If still tied (e.g., multiple flows never seen before), the flow with the higher Priority setting (configured in Flow settings) triggers first.
If priorities are tied, the flow created earliest (with the oldest creation date) is prioritized.
Taking action
Once the Debugger shows you the specific red condition(s) blocking the flow, you can:
Adjust the auto-start conditions of the flow in the Userflow builder to better match your requirements.
Verify that the required user attributes, events, or page states are implemented correctly in your application. After making updates, re-check the conditions using the Debugger to confirm the pills turn Green and the flow triggers as expected.